Why it’s critical to manage pulsation issues in reciprocating pumps:
The back-and-forth see-saw effect of pulsation can cause pumps to stop working well. Over time, it damages critical system components. In reciprocating pumps, also called positive displacement pumps this issue leads to performance and longevity problems.
Power Flow’s oilfield pump engineers can help.
Power Flow Solves Pulsation Problems
We offer cost-effective, lightweight options to manage your reciprocating pump’s pulsation issues.
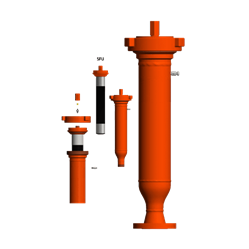
We now provide the formerly Coorstek dampeners in various design profiles.
Replace your existing appendage or bladder-designed pulsation dampener with these cost-effective, easy-to-install options.
 The following and additional Coorstek Series Dampeners are now available through Power-Flow:
The following and additional Coorstek Series Dampeners are now available through Power-Flow:
Coorstek Series Model* | Volume
-
C C-1501-F | 35 cubic inch
-
U U-4501-T | 100 cubic inch
-
ST ST-7002-F | 300 cubic inch
-
T T-14004-F | 600 cubic inch
-
M M-1504-F | 900 & 1200 cubic inch
*Additional model numbers are also available through Power-Flow
- Volumes from 23 cubic inch to 1200 cubic inch
- Bladder type – gas-filled design
- Great performance in an affordable and durable package
- A top-repairable/serviceable design for quick access
- Flow-through & maintenance-free styles available
Pulsation Management Equipment Parts
Dampeners or Snubbers
These devices use a nitrogen-charged bladder to absorb the pressure spikes and surges created by reciprocating pumps. They help reduce pulsations from 45% down to as low as 2%.
-
Dampener Applications:
- Suction stabilizer
- Discharge dampener
- Surge protection
- Thermal/volume expansion compensators
- Flow measurement
-
Dampener Design Types: Small and lightweight for easy installation.
-
- Bladder/cartridge (elastomer)
- Diaphragm
- Bellows
- Gas-Free (Cellular or Fluid)
Performance Issues
-
Vibration
Pulsation causes vibrations throughout the pump and associated piping, contributing to premature wear and potential failure of pump components. The system’s rapid fluid flow and pressure changes will cause this vibration.
-
Cavitation
Another consequence of pulsation is cavitation, where rapid pressure changes create bubbles in the liquid. These bubbles can implode violently near pump impellers and bearings, causing damage and reducing pump efficiency.
-
Noise
Pulsation generates noise that can be disruptive to operators and nearby residents. Excessive noise can mask important operational sounds that might indicate underlying pump issues requiring attention.
Managing Pulsation Pressure
To mitigate the adverse effects, dampeners can be installed at the discharge side of reciprocating pumps. These devices help regulate pressure and flow variations, thereby prolonging the pump’s service life.
How Pulsation Dampeners Work
Dampeners act as shock absorbers filled with compressed gas and process fluid, separated by a flexible bladder or diaphragm. They effectively smooth out pressure spikes and fluctuations caused by the pump’s reciprocating action.
Vulnerable Components
Components such as valves, seals, bearings, and piping are particularly susceptible to damage from the dynamic forces induced by pulsating flow. Over time, this wear can lead to diminished pump performance, increased maintenance needs, and premature equipment failure.
Power Flow sells dampeners to fit reciprocating pumps from the following manufacturers: